Jonathan Noonan, Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute and Karlheinz Peter, Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute
Repeated COVID-19 outbreaks in Australia have once again highlighted the need for rapid and widespread vaccination. We are extremely fortunate the global scientific community has been able to develop a handful of highly effective vaccines in such a short time.
As with any vaccine or medicine, the COVID vaccines do carry small risks. The rare blood clotting disorder caused by the AstraZeneca vaccine — thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome, or TTS — has largely dominated the headlines.
But we’re also seeing reports of a potentially increased risk of myocarditis and pericarditis (heart inflammation) following the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, developed by Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna.
Here’s why this shouldn’t be cause for concern.
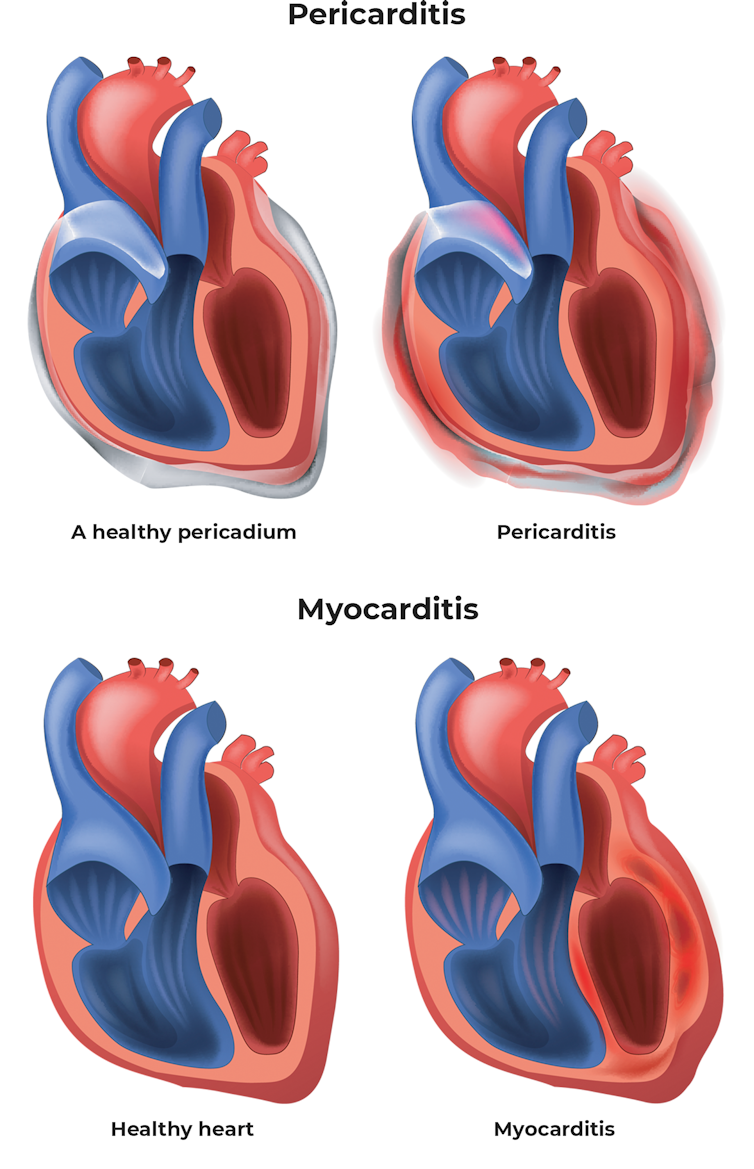
First, what are myocarditis and pericarditis?
There are three main types of heart inflammation: endocarditis, myocarditis, and pericarditis. These involve inflammation of the inner lining of the heart, the heart muscle, and the outer lining of the heart respectively.
Viruses, including the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19, are the most common cause of myocarditis and pericarditis. Essentially, the inflammation the immune system generates to combat infections can inadvertently lead to inflammation of the heart.
In the very rare cases of myocarditis and pericarditis observed after vaccination with a COVID mRNA shot, it’s possible a similar thing might be happening. That is, the vaccine causes the immune system to generate some level of inflammation so it’s prepared to mount a response against SARS-CoV-2, and this inflammation is partially misdirected to the heart.
But the risk is very small, and the conditions are treatable.
What’s the risk?
The exact incidence of myocarditis and pericarditis following vaccination is still being defined, and it remains to be proven that mRNA vaccines are truly the cause of these conditions — although it seems likely.
In Australia, of roughly 3.7 million doses of the Pfizer vaccine administered up to July 11, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) reports there have been 50 cases of suspected myocarditis or pericarditis. This suggests a risk of one per 74,000 vaccines. The TGA notes most people who developed these conditions have recovered or are recovering.
However, given the relatively small number of vaccinations administered in Australia, it’s important to consider more complete data from countries with higher vaccination rates.
The United States’ Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) had received 1,226 reports of myocarditis following 296 million doses of mRNA vaccines administered up to June 11. This equates to a risk of roughly one in 240,000 doses. These cases were mostly in young men and predominantly occurred after the second dose.
Independently from vaccines, myocarditis occurs in roughly 23 per 100,000 people worldwide per year (we don’t have reliable figures for pericarditis). This shows us there’s a much lower risk from vaccination than exists in the population generally.
Symptoms to look out for
Normal side effects of COVID-19 vaccines include headache, fever, chills, muscle or joint pain, fatigue and nausea.
In contrast, chest pain, irregular heartbeat, heart palpitations, shortness of breath and light-headedness could indicate myocarditis or pericarditis. Symptoms of these conditions have generally occurred within seven days of vaccination. Anyone who experiences these symptoms should seek medical attention.
In most cases, myocarditis and pericarditis can be successfully treated with anti-inflammatory drugs, such as aspirin and corticosteroids.
In Israel, 95% of cases recently investigated were classified as mild. Similarly, the CDC has reported most patients in the US have recovered quickly.
While this very small risk of heart inflammation following vaccination may be alarming, it’s crucial to understand the risk of heart damage following severe COVID-19 is far greater.
COVID-19 and heart damage
Damage of the heart muscle is a common consequence of coronavirus. Research shows it occurs in up to 28% of patients hospitalised with COVID-19.
Importantly, the risk of death is markedly higher in COVID-19 patients who sustain heart muscle damage. While we need further research to understand precisely how COVID-19 damages the heart, myocarditis and pericarditis are major causes of the heart damage found in COVID-19 patients.
The benefit outweighs the risk
The recent limits applied to the use of the AstraZeneca vaccine in younger age groups suggests the relatively low risk of COVID-19 in Australia justifies being highly selective over vaccine use.
But while Australia has done incredibly well at containing COVID-19, the risk of transmission here remains high given the global COVID-19 situation. We’re seeing this daily as we contend with outbreaks and lockdowns around the country.
Myocarditis and pericarditis are potentially associated with the mRNA vaccines, but these complications are extremely rare, most often mild, and seem to be treatable.
As has been the consistent message from the medical and scientific communities throughout this pandemic, the benefit of COVID-19 vaccines significantly outweighs the risk of rare side effects. This is particularly true for the highly effective mRNA-based vaccines as COVID-19 continues to spread around the world.
Jonathan Noonan, Research Officer, Atherothrombosis and Vascular Biology Laboratory, Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute and Karlheinz Peter, Interventional Cardiologist, Alfred Hospital; Professor of Medicine and Immunology, Monash University; Professor and Head, Department of Cardiometabolic Health, University of Melbourne; Lab Head, Atherothrombosis and Vascular Biology and Deputy Director, Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.